OAuth 2.0 资源服务器不透明令牌
内省的最小依赖项
如 JWT 的最小依赖项 中所述,大多数资源服务器支持都集中在 spring-security-oauth2-resource-server 中。但是,除非提供了自定义的 OpaqueTokenIntrospector,否则资源服务器将回退到 SpringOpaqueTokenIntrospector。这意味着只需要 spring-security-oauth2-resource-server 就可以拥有一个支持不透明不记名令牌的最小工作资源服务器。
内省的最小配置
通常,不透明令牌可以通过授权服务器托管的 OAuth 2.0 内省端点 进行验证。当需要撤销时,这会非常方便。
使用 Spring Boot 时,将应用程序配置为使用内省的资源服务器包括两个基本步骤。首先,包括所需的依赖项;其次,指明内省端点详细信息。
指定授权服务器
要指定内省端点在哪里,只需执行以下操作
spring:
security:
oauth2:
resourceserver:
opaquetoken:
introspection-uri: https://idp.example.com/introspect
client-id: client
client-secret: secret其中 idp.example.com/introspect 是您的授权服务器托管的内省端点,client-id 和 client-secret 是访问该端点所需的凭据。
资源服务器将使用这些属性进行进一步的自配置,并随后验证传入的 JWT。
| 使用内省时,授权服务器的说法就是法律。如果授权服务器响应令牌有效,那么它就是有效的。 |
就是这样!
运行时预期
应用程序启动后,资源服务器将尝试处理包含 Authorization: Bearer 头的任何请求
GET / HTTP/1.1
Authorization: Bearer some-token-value # Resource Server will process this只要指示了此方案,资源服务器就会尝试根据不记名令牌规范处理请求。
给定一个不透明令牌,资源服务器将
-
使用提供的凭据和令牌查询提供的内省端点
-
检查响应中是否存在
{ 'active' : true }属性 -
将每个范围映射到带有前缀
SCOPE_的权限
默认情况下,生成的 Authentication#getPrincipal 是 Spring Security OAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal 对象,如果存在,Authentication#getName 映射到令牌的 sub 属性。
从这里,您可能需要跳转到
不透明令牌身份验证的工作原理
接下来,让我们看看 Spring Security 用于支持 servlet 应用程序(就像我们刚刚看到的那个)中的 不透明令牌 身份验证的架构组件。
OpaqueTokenAuthenticationProvider 是一个 AuthenticationProvider 实现,它利用 OpaqueTokenIntrospector 来验证不透明令牌。
让我们看看 OpaqueTokenAuthenticationProvider 在 Spring Security 中是如何工作的。该图解释了 读取不记名令牌 中的 AuthenticationManager 的工作细节。
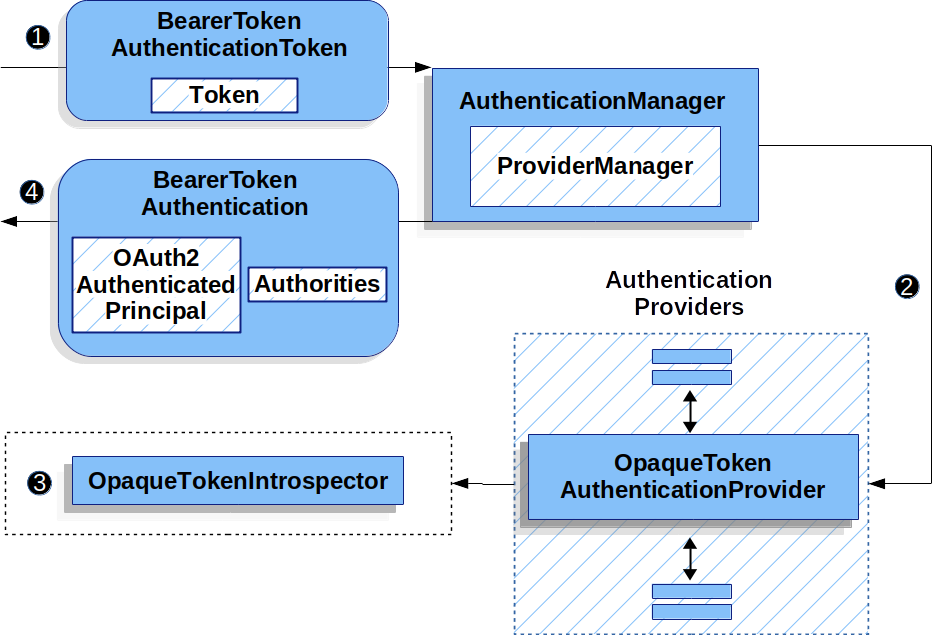
OpaqueTokenAuthenticationProvider 用法![]() 读取不记名令牌 中的身份验证
读取不记名令牌 中的身份验证 Filter 将 BearerTokenAuthenticationToken 传递给由 ProviderManager 实现的 AuthenticationManager。
![]()
ProviderManager 配置为使用类型为 OpaqueTokenAuthenticationProvider 的 AuthenticationProvider。
![]()
OpaqueTokenAuthenticationProvider 使用 OpaqueTokenIntrospector 内省不透明令牌并添加授予的权限。当身份验证成功时,返回的 Authentication 类型为 BearerTokenAuthentication,其 principal 是由配置的 OpaqueTokenIntrospector 返回的 OAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal,并且具有至少包含 FACTOR_BEARER 的一组权限。最终,返回的 BearerTokenAuthentication 将由身份验证 Filter 设置在 SecurityContextHolder 上。
身份验证后查找属性
令牌通过身份验证后,BearerTokenAuthentication 实例将设置在 SecurityContext 中。
这意味着在使用 @EnableWebMvc 进行配置时,它在 @Controller 方法中可用
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@GetMapping("/foo")
public String foo(BearerTokenAuthentication authentication) {
return authentication.getTokenAttributes().get("sub") + " is the subject";
}@GetMapping("/foo")
fun foo(authentication: BearerTokenAuthentication): String {
return authentication.tokenAttributes["sub"].toString() + " is the subject"
}由于 BearerTokenAuthentication 持有 OAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal,这也意味着它也适用于控制器方法
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@GetMapping("/foo")
public String foo(@AuthenticationPrincipal OAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal principal) {
return principal.getAttribute("sub") + " is the subject";
}@GetMapping("/foo")
fun foo(@AuthenticationPrincipal principal: OAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal): String {
return principal.getAttribute<Any>("sub").toString() + " is the subject"
}通过 SpEL 查找属性
当然,这也意味着可以通过 SpEL 访问属性。
例如,如果使用 @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity 以便可以使用 @PreAuthorize 注解,则可以这样做
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@PreAuthorize("principal?.attributes['sub'] == 'foo'")
public String forFoosEyesOnly() {
return "foo";
}@PreAuthorize("principal?.attributes['sub'] == 'foo'")
fun forFoosEyesOnly(): String {
return "foo"
}覆盖或替换 Boot 自动配置
Spring Boot 代表资源服务器生成了两个 @Bean。
第一个是 SecurityFilterChain,它将应用程序配置为资源服务器。当使用不透明令牌时,此 SecurityFilterChain 看起来像
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize
.anyRequest().authenticated()
)
.oauth2ResourceServer((oauth2) -> oauth2
.opaqueToken(Customizer.withDefaults())
);
return http.build();
}@Bean
open fun filterChain(http: HttpSecurity): SecurityFilterChain {
http {
authorizeHttpRequests {
authorize(anyRequest, authenticated)
}
oauth2ResourceServer {
opaqueToken { }
}
}
return http.build()
}如果应用程序不暴露 SecurityFilterChain bean,则 Spring Boot 将暴露上述默认的 bean。
替换它就像在应用程序中暴露 bean 一样简单
-
Java
-
Kotlin
import static org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.authorization.OAuth2AuthorizationManagers.hasScope;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class MyCustomSecurityConfiguration {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize
.requestMatchers("/messages/**").access(hasScope("message:read"))
.anyRequest().authenticated()
)
.oauth2ResourceServer((oauth2) -> oauth2
.opaqueToken((opaqueToken) -> opaqueToken
.introspector(myIntrospector())
)
);
return http.build();
}
}import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.authorization.OAuth2AuthorizationManagers.hasScope;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
class MyCustomSecurityConfiguration {
@Bean
open fun filterChain(http: HttpSecurity): SecurityFilterChain {
http {
authorizeHttpRequests {
authorize("/messages/**", hasScope("SCOPE_message:read"))
authorize(anyRequest, authenticated)
}
oauth2ResourceServer {
opaqueToken {
introspector = myIntrospector()
}
}
}
return http.build()
}
}上述代码要求任何以 /messages/ 开头的 URL 都具有 message:read 范围。
oauth2ResourceServer DSL 上的方法也将覆盖或替换自动配置。
例如,Spring Boot 创建的第二个 @Bean 是一个 OpaqueTokenIntrospector,它将 String 令牌解码为经过验证的 OAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal 实例
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Bean
public OpaqueTokenIntrospector introspector() {
return SpringOpaqueTokenIntrospector.withIntrospectionUri(introspectionUri)
.clientId(clientId).clientSecret(clientSecret).build();
}@Bean
fun introspector(): OpaqueTokenIntrospector {
return SpringOpaqueTokenIntrospector.withIntrospectionUri(introspectionUri)
.clientId(clientId).clientSecret(clientSecret).build()
}如果应用程序没有暴露 OpaqueTokenIntrospector bean,那么 Spring Boot 将暴露上述默认的 bean。
并且其配置可以通过 introspectionUri() 和 introspectionClientCredentials() 进行覆盖,或者通过 introspector() 进行替换。
如果应用程序不暴露 OpaqueTokenAuthenticationConverter bean,那么 spring-security 将构建 BearerTokenAuthentication。
或者,如果您根本不使用 Spring Boot,那么所有这些组件——过滤器链、OpaqueTokenIntrospector 和 OpaqueTokenAuthenticationConverter——都可以在 XML 中指定。
过滤器链指定如下
-
Xml
<http>
<intercept-uri pattern="/**" access="authenticated"/>
<oauth2-resource-server>
<opaque-token introspector-ref="opaqueTokenIntrospector"
authentication-converter-ref="opaqueTokenAuthenticationConverter"/>
</oauth2-resource-server>
</http>而 OpaqueTokenIntrospector 则指定如下
-
Xml
<bean id="opaqueTokenIntrospector"
class="org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.resource.introspection.SpringOpaqueTokenIntrospector">
<constructor-arg value="${spring.security.oauth2.resourceserver.opaquetoken.introspection_uri}"/>
<constructor-arg value="${spring.security.oauth2.resourceserver.opaquetoken.client_id}"/>
<constructor-arg value="${spring.security.oauth2.resourceserver.opaquetoken.client_secret}"/>
</bean>而 OpaqueTokenAuthenticationConverter 则指定如下
-
Xml
<bean id="opaqueTokenAuthenticationConverter"
class="com.example.CustomOpaqueTokenAuthenticationConverter"/>使用 introspectionUri()
授权服务器的内省 URI 可以 作为配置属性 进行配置,也可以在 DSL 中提供
-
Java
-
Kotlin
-
Xml
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class DirectlyConfiguredIntrospectionUri {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize
.anyRequest().authenticated()
)
.oauth2ResourceServer((oauth2) -> oauth2
.opaqueToken((opaqueToken) -> opaqueToken
.introspectionUri("https://idp.example.com/introspect")
.introspectionClientCredentials("client", "secret")
)
);
return http.build();
}
}@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
class DirectlyConfiguredIntrospectionUri {
@Bean
open fun filterChain(http: HttpSecurity): SecurityFilterChain {
http {
authorizeHttpRequests {
authorize(anyRequest, authenticated)
}
oauth2ResourceServer {
opaqueToken {
introspectionUri = "https://idp.example.com/introspect"
introspectionClientCredentials("client", "secret")
}
}
}
return http.build()
}
}<bean id="opaqueTokenIntrospector"
class="org.springframework.security.oauth2.server.resource.introspection.SpringOpaqueTokenIntrospector">
<constructor-arg value="https://idp.example.com/introspect"/>
<constructor-arg value="client"/>
<constructor-arg value="secret"/>
</bean>使用 introspectionUri() 优先于任何配置属性。
使用 introspector()
比 introspectionUri() 更强大的是 introspector(),它将完全取代任何 Boot 自动配置的 OpaqueTokenIntrospector
-
Java
-
Kotlin
-
Xml
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class DirectlyConfiguredIntrospector {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize
.anyRequest().authenticated()
)
.oauth2ResourceServer((oauth2) -> oauth2
.opaqueToken((opaqueToken) -> opaqueToken
.introspector(myCustomIntrospector())
)
);
return http.build();
}
}@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
class DirectlyConfiguredIntrospector {
@Bean
open fun filterChain(http: HttpSecurity): SecurityFilterChain {
http {
authorizeHttpRequests {
authorize(anyRequest, authenticated)
}
oauth2ResourceServer {
opaqueToken {
introspector = myCustomIntrospector()
}
}
}
return http.build()
}
}<http>
<intercept-uri pattern="/**" access="authenticated"/>
<oauth2-resource-server>
<opaque-token introspector-ref="myCustomIntrospector"/>
</oauth2-resource-server>
</http>暴露一个 OpaqueTokenIntrospector @Bean
或者,暴露一个 OpaqueTokenIntrospector @Bean 具有与 introspector() 相同的效果
@Bean
public OpaqueTokenIntrospector introspector() {
return return SpringOpaqueTokenIntrospector.withIntrospectionUri(introspectionUri)
.clientId(clientId).clientSecret(clientSecret).build();
}配置授权
OAuth 2.0 内省端点通常会返回一个 scope 属性,指示授予的范围(或权限),例如
{ …, "scope" : "messages contacts"}
在这种情况下,资源服务器将尝试将这些范围强制转换为授予权限列表,为每个范围添加前缀字符串 "SCOPE_"。
这意味着要使用不透明令牌派生的范围保护端点或方法,相应的表达式应包含此前缀
-
Java
-
Kotlin
-
Xml
import static org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.authorization.OAuth2AuthorizationManagers.hasScope;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class MappedAuthorities {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests((authorizeRequests) -> authorizeRequests
.requestMatchers("/contacts/**").access(hasScope("contacts"))
.requestMatchers("/messages/**").access(hasScope("messages"))
.anyRequest().authenticated()
)
.oauth2ResourceServer((oauth2) -> oauth2
.opaqueToken(Customizer.withDefaults())
);
return http.build();
}
}import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.authorization.OAuth2AuthorizationManagers.hasScope
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
class MappedAuthorities {
@Bean
open fun filterChain(http: HttpSecurity): SecurityFilterChain {
http {
authorizeHttpRequests {
authorize("/contacts/**", hasScope("contacts"))
authorize("/messages/**", hasScope("messages"))
authorize(anyRequest, authenticated)
}
oauth2ResourceServer {
opaqueToken { }
}
}
return http.build()
}
}<http>
<intercept-uri pattern="/contacts/**" access="hasAuthority('SCOPE_contacts')"/>
<intercept-uri pattern="/messages/**" access="hasAuthority('SCOPE_messages')"/>
<oauth2-resource-server>
<opaque-token introspector-ref="opaqueTokenIntrospector"/>
</oauth2-resource-server>
</http>或者类似地使用方法安全
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('SCOPE_messages')")
public List<Message> getMessages(...) {}@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('SCOPE_messages')")
fun getMessages(): List<Message?> {}手动提取权限
默认情况下,不透明令牌支持将从内省响应中提取 scope 声明并将其解析为单独的 GrantedAuthority 实例。
例如,如果内省响应是
{
"active" : true,
"scope" : "message:read message:write"
}那么资源服务器将生成一个具有两个权限的 Authentication,一个用于 message:read,另一个用于 message:write。
当然,这可以通过使用自定义的 OpaqueTokenIntrospector 进行自定义,该内省器会查看属性集并以自己的方式进行转换
-
Java
-
Kotlin
public class CustomAuthoritiesOpaqueTokenIntrospector implements OpaqueTokenIntrospector {
private OpaqueTokenIntrospector delegate = SpringOpaqueTokenIntrospector
.withIntrospectionUri("https://idp.example.org/introspect")
.clientId("client").clientSecret("secret").build();
public OAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal introspect(String token) {
OAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal principal = this.delegate.introspect(token);
return new DefaultOAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal(
principal.getName(), principal.getAttributes(), extractAuthorities(principal));
}
private Collection<GrantedAuthority> extractAuthorities(OAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal principal) {
List<String> scopes = principal.getAttribute(OAuth2IntrospectionClaimNames.SCOPE);
return scopes.stream()
.map(SimpleGrantedAuthority::new)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}class CustomAuthoritiesOpaqueTokenIntrospector : OpaqueTokenIntrospector {
private val delegate: OpaqueTokenIntrospector = SpringOpaqueTokenIntrospector
.withIntrospectionUri("https://idp.example.org/introspect")
.clientId("client").clientSecret("secret").build()
override fun introspect(token: String): OAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal {
val principal: OAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal = delegate.introspect(token)
return DefaultOAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal(
principal.name, principal.attributes, extractAuthorities(principal))
}
private fun extractAuthorities(principal: OAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal): Collection<GrantedAuthority> {
val scopes: List<String> = principal.getAttribute(OAuth2IntrospectionClaimNames.SCOPE)
return scopes
.map { SimpleGrantedAuthority(it) }
}
}此后,只需将其公开为 @Bean 即可配置此自定义内省器
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Bean
public OpaqueTokenIntrospector introspector() {
return new CustomAuthoritiesOpaqueTokenIntrospector();
}@Bean
fun introspector(): OpaqueTokenIntrospector {
return CustomAuthoritiesOpaqueTokenIntrospector()
}配置超时
默认情况下,资源服务器与授权服务器协调时,连接超时和套接字超时各为 30 秒。
在某些情况下,这可能太短了。此外,它没有考虑更复杂的模式,如回退和发现。
为了调整资源服务器连接授权服务器的方式,SpringOpaqueTokenIntrospector 接受 RestOperations 实例
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Bean
public OpaqueTokenIntrospector introspector(RestTemplateBuilder builder, OAuth2ResourceServerProperties properties) {
RestOperations rest = builder
.basicAuthentication(properties.getOpaquetoken().getClientId(), properties.getOpaquetoken().getClientSecret())
.setConnectTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(60))
.setReadTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(60))
.build();
return SpringOpaqueTokenIntrospector(introspectionUri, rest);
}@Bean
fun introspector(builder: RestTemplateBuilder, properties: OAuth2ResourceServerProperties): OpaqueTokenIntrospector? {
val rest: RestOperations = builder
.basicAuthentication(properties.opaquetoken.clientId, properties.opaquetoken.clientSecret)
.setConnectTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(60))
.setReadTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(60))
.build()
return SpringOpaqueTokenIntrospector(introspectionUri, rest)
}将内省与 JWT 结合使用
一个常见的问题是内省是否与 JWT 兼容。Spring Security 的不透明令牌支持被设计为不关心令牌的格式——它会很高兴地将任何令牌传递给所提供的内省端点。
因此,假设您有一个要求,需要在每个请求中检查授权服务器,以防 JWT 已被吊销。
即使您使用 JWT 格式的令牌,您的验证方法是内省,这意味着您需要这样做
spring:
security:
oauth2:
resourceserver:
opaquetoken:
introspection-uri: https://idp.example.org/introspection
client-id: client
client-secret: secret在这种情况下,结果 Authentication 将是 BearerTokenAuthentication。相应 OAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal 中的任何属性都将是内省端点返回的任何内容。
但是,奇怪的是,内省端点只返回令牌是否活跃。现在怎么办?
在这种情况下,您可以创建一个自定义的 OpaqueTokenIntrospector,它仍然会访问该端点,但随后会将返回的 principal 更新为具有 JWT 声明作为属性
-
Java
-
Kotlin
public class JwtOpaqueTokenIntrospector implements OpaqueTokenIntrospector {
private OpaqueTokenIntrospector delegate = SpringOpaqueTokenIntrospector
.withIntrospectionUri("https://idp.example.org/introspect")
.clientId("client").clientSecret("secret").build();
private JwtDecoder jwtDecoder = new NimbusJwtDecoder(new ParseOnlyJWTProcessor());
public OAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal introspect(String token) {
OAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal principal = this.delegate.introspect(token);
try {
Jwt jwt = this.jwtDecoder.decode(token);
return new DefaultOAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal(jwt.getClaims(), NO_AUTHORITIES);
} catch (JwtException ex) {
throw new OAuth2IntrospectionException(ex);
}
}
private static class ParseOnlyJWTProcessor extends DefaultJWTProcessor<SecurityContext> {
JWTClaimsSet process(SignedJWT jwt, SecurityContext context)
throws JOSEException {
return jwt.getJWTClaimsSet();
}
}
}class JwtOpaqueTokenIntrospector : OpaqueTokenIntrospector {
private val delegate: OpaqueTokenIntrospector = SpringOpaqueTokenIntrospector
.withIntrospectionUri("https://idp.example.org/introspect")
.clientId("client").clientSecret("secret").build()
private val jwtDecoder: JwtDecoder = NimbusJwtDecoder(ParseOnlyJWTProcessor())
override fun introspect(token: String): OAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal {
val principal = delegate.introspect(token)
return try {
val jwt: Jwt = jwtDecoder.decode(token)
DefaultOAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal(jwt.claims, NO_AUTHORITIES)
} catch (ex: JwtException) {
throw OAuth2IntrospectionException(ex.message)
}
}
private class ParseOnlyJWTProcessor : DefaultJWTProcessor<SecurityContext>() {
override fun process(jwt: SignedJWT, context: SecurityContext): JWTClaimsSet {
return jwt.jwtClaimsSet
}
}
}此后,只需将其公开为 @Bean 即可配置此自定义内省器
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Bean
public OpaqueTokenIntrospector introspector() {
return new JwtOpaqueTokenIntrospector();
}@Bean
fun introspector(): OpaqueTokenIntrospector {
return JwtOpaqueTokenIntrospector()
}调用 /userinfo 端点
一般来说,资源服务器不关心底层用户,而是关心已授予的权限。
尽管如此,有时将授权语句与用户关联起来可能很有价值。
如果应用程序也使用 spring-security-oauth2-client 并设置了适当的 ClientRegistrationRepository,那么使用自定义的 OpaqueTokenIntrospector 就可以非常简单地实现。下面的实现做了三件事
-
委托给内省端点,以确认令牌的有效性
-
查找与
/userinfo端点关联的适当客户端注册 -
调用并返回
/userinfo端点的响应
-
Java
-
Kotlin
public class UserInfoOpaqueTokenIntrospector implements OpaqueTokenIntrospector {
private final OpaqueTokenIntrospector delegate = SpringOpaqueTokenIntrospector
.withIntrospectionUri("https://idp.example.org/introspect")
.clientId("client").clientSecret("secret").build();
private final OAuth2UserService oauth2UserService = new DefaultOAuth2UserService();
private final ClientRegistrationRepository repository;
// ... constructor
@Override
public OAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal introspect(String token) {
OAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal authorized = this.delegate.introspect(token);
Instant issuedAt = authorized.getAttribute(ISSUED_AT);
Instant expiresAt = authorized.getAttribute(EXPIRES_AT);
ClientRegistration clientRegistration = this.repository.findByRegistrationId("registration-id");
OAuth2AccessToken token = new OAuth2AccessToken(BEARER, token, issuedAt, expiresAt);
OAuth2UserRequest oauth2UserRequest = new OAuth2UserRequest(clientRegistration, token);
return this.oauth2UserService.loadUser(oauth2UserRequest);
}
}class UserInfoOpaqueTokenIntrospector : OpaqueTokenIntrospector {
private val delegate: OpaqueTokenIntrospector = SpringOpaqueTokenIntrospector
.withIntrospectionUri("https://idp.example.org/introspect")
.clientId("client").clientSecret("secret").build()
private val oauth2UserService = DefaultOAuth2UserService()
private val repository: ClientRegistrationRepository? = null
// ... constructor
override fun introspect(token: String): OAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal {
val authorized = delegate.introspect(token)
val issuedAt: Instant? = authorized.getAttribute(ISSUED_AT)
val expiresAt: Instant? = authorized.getAttribute(EXPIRES_AT)
val clientRegistration: ClientRegistration = repository!!.findByRegistrationId("registration-id")
val accessToken = OAuth2AccessToken(BEARER, token, issuedAt, expiresAt)
val oauth2UserRequest = OAuth2UserRequest(clientRegistration, accessToken)
return oauth2UserService.loadUser(oauth2UserRequest)
}
}如果您根本不使用 spring-security-oauth2-client,它仍然很简单。您只需使用自己的 WebClient 实例调用 /userinfo
-
Java
-
Kotlin
public class UserInfoOpaqueTokenIntrospector implements OpaqueTokenIntrospector {
private final OpaqueTokenIntrospector delegate = SpringOpaqueTokenIntrospector
.withIntrospectionUri("https://idp.example.org/introspect")
.clientId("client").clientSecret("secret").build();
private final WebClient rest = WebClient.create();
@Override
public OAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal introspect(String token) {
OAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal authorized = this.delegate.introspect(token);
return makeUserInfoRequest(authorized);
}
}class UserInfoOpaqueTokenIntrospector : OpaqueTokenIntrospector {
private val delegate: OpaqueTokenIntrospector = SpringOpaqueTokenIntrospector
.withIntrospectionUri("https://idp.example.org/introspect")
.clientId("client").clientSecret("secret").build()
private val rest: WebClient = WebClient.create()
override fun introspect(token: String): OAuth2AuthenticatedPrincipal {
val authorized = delegate.introspect(token)
return makeUserInfoRequest(authorized)
}
}无论哪种方式,创建 OpaqueTokenIntrospector 后,您都应该将其作为 @Bean 发布以覆盖默认值
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Bean
OpaqueTokenIntrospector introspector() {
return new UserInfoOpaqueTokenIntrospector(...);
}@Bean
fun introspector(): OpaqueTokenIntrospector {
return UserInfoOpaqueTokenIntrospector(...)
}
