架构
过滤器回顾
Spring Security 的 Servlet 支持基于 Servlet 过滤器,因此首先了解过滤器的作用很有帮助。下图显示了单个 HTTP 请求的处理程序的典型分层。
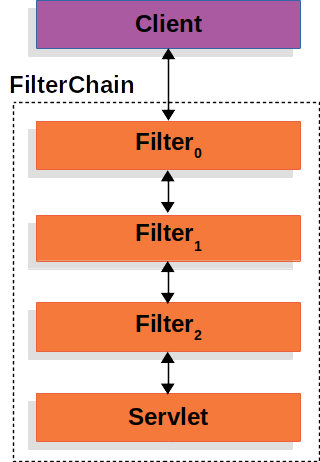
客户端向应用程序发送请求,容器根据请求 URI 的路径创建一个 FilterChain,其中包含应处理 HttpServletRequest 的 Filter 实例和 Servlet。在 Spring MVC 应用程序中,Servlet 是 DispatcherServlet 的一个实例。最多只有一个 Servlet 可以处理单个 HttpServletRequest 和 HttpServletResponse。但是,可以使用多个 Filter 来
-
阻止下游
Filter实例或Servlet被调用。在这种情况下,Filter通常会写入HttpServletResponse。 -
修改下游
Filter实例和Servlet使用的HttpServletRequest或HttpServletResponse。
Filter 的强大之处在于传递给它的 FilterChain。
FilterChain 使用示例-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
// do something before the rest of the application
chain.doFilter(request, response); // invoke the rest of the application
// do something after the rest of the application
}@Throws(IOException::class, ServletException::class)
override fun doFilter(request: ServletRequest?, response: ServletResponse?, chain: FilterChain) {
// do something before the rest of the application
chain.doFilter(request, response) // invoke the rest of the application
// do something after the rest of the application
}由于 Filter 仅影响下游 Filter 实例和 Servlet,因此每个 Filter 被调用的顺序至关重要。
DelegatingFilterProxy
Spring 提供了一个名为 DelegatingFilterProxy 的 Filter 实现,它允许在 Servlet 容器的生命周期和 Spring 的 ApplicationContext 之间架起桥梁。Servlet 容器允许使用其自身的标准注册 Filter 实例,但它不了解 Spring 定义的 Bean。您可以通过标准 Servlet 容器机制注册 DelegatingFilterProxy,但将所有工作委托给实现 Filter 的 Spring Bean。
下图显示了 DelegatingFilterProxy 如何融入 Filter 实例和 FilterChain。
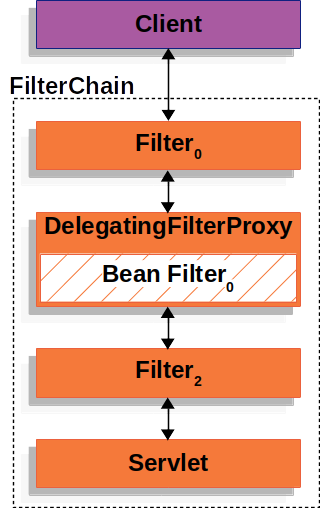
DelegatingFilterProxy 从 ApplicationContext 中查找 Bean Filter0,然后调用 Bean Filter0。以下清单显示了 DelegatingFilterProxy 的伪代码
DelegatingFilterProxy 伪代码-
Java
-
Kotlin
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) {
Filter delegate = getFilterBean(someBeanName); (1)
delegate.doFilter(request, response); (2)
}fun doFilter(request: ServletRequest, response: ServletResponse, chain: FilterChain) {
val delegate: Filter = getFilterBean(someBeanName) (1)
delegate.doFilter(request, response) (2)
}| 1 | 惰性获取作为 Spring Bean 注册的 Filter。对于 DelegatingFilterProxy 中的示例,delegate 是 Bean Filter0 的一个实例。 |
| 2 | 将工作委托给 Spring Bean。 |
DelegatingFilterProxy 的另一个好处是它允许延迟查找 Filter bean 实例。这很重要,因为容器需要在启动之前注册 Filter 实例。然而,Spring 通常使用 ContextLoaderListener 加载 Spring Bean,这直到 Filter 实例需要注册之后才完成。
FilterChainProxy
Spring Security 的 Servlet 支持包含在 FilterChainProxy 中。FilterChainProxy 是 Spring Security 提供的一个特殊 Filter,它允许通过 SecurityFilterChain 将工作委托给许多 Filter 实例。由于 FilterChainProxy 是一个 Bean,它通常被包装在 DelegatingFilterProxy 中。
下图显示了 FilterChainProxy 的作用。
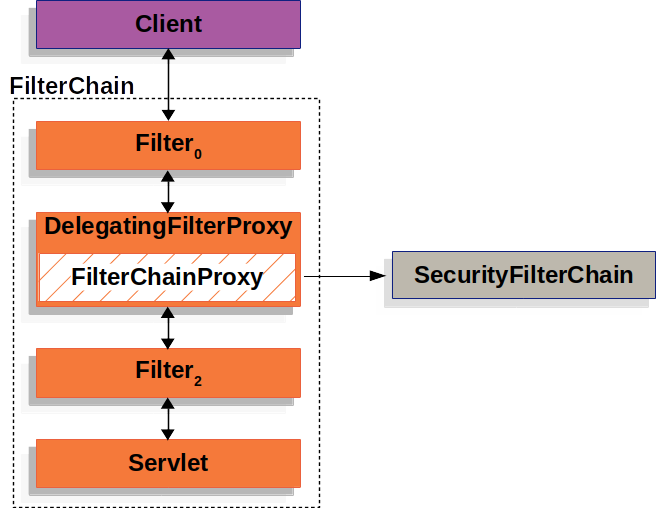
SecurityFilterChain
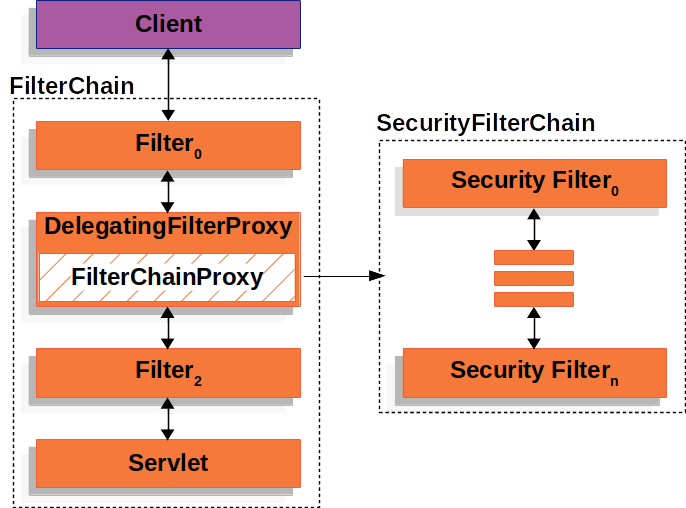
SecurityFilterChain 由 FilterChainProxy 使用,用于确定应为当前请求调用哪些 Spring Security Filter 实例。
下图显示了 SecurityFilterChain 的作用。
SecurityFilterChain 中的 安全过滤器 通常是 Bean,但它们注册到 FilterChainProxy 而不是 DelegatingFilterProxy。FilterChainProxy 相比直接注册到 Servlet 容器或 DelegatingFilterProxy 提供了许多优势。首先,它为 Spring Security 的所有 Servlet 支持提供了一个起点。因此,如果您尝试对 Spring Security 的 Servlet 支持进行故障排除,在 FilterChainProxy 中添加一个调试点是一个很好的开始。
其次,由于 FilterChainProxy 是 Spring Security 使用的核心,它可以执行非可选的任务。例如,它清除 SecurityContext 以避免内存泄漏。它还应用 Spring Security 的 HttpFirewall 来保护应用程序免受某些类型的攻击。
此外,它在确定何时应调用 SecurityFilterChain 方面提供了更大的灵活性。在 Servlet 容器中,Filter 实例仅根据 URL 调用。然而,FilterChainProxy 可以通过使用 RequestMatcher 接口根据 HttpServletRequest 中的任何内容确定调用。
下图显示了多个 SecurityFilterChain 实例
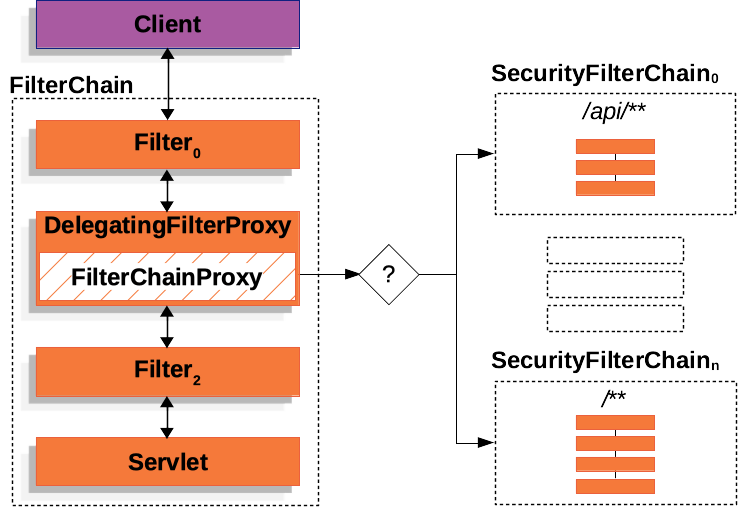
在 多个 SecurityFilterChain 图中,FilterChainProxy 决定应该使用哪个 SecurityFilterChain。只有第一个匹配的 SecurityFilterChain 被调用。如果请求的 URL 是 /api/messages/,它首先匹配 SecurityFilterChain0 的模式 /api/**,因此只调用 SecurityFilterChain0,即使它也匹配 SecurityFilterChainn。如果请求的 URL 是 /messages/,它不匹配 SecurityFilterChain0 的模式 /api/**,因此 FilterChainProxy 继续尝试每个 SecurityFilterChain。假设没有其他 SecurityFilterChain 实例匹配,则调用 SecurityFilterChainn。
请注意,SecurityFilterChain0 只配置了三个安全 Filter 实例。然而,SecurityFilterChainn 配置了四个安全 Filter 实例。重要的是要注意,每个 SecurityFilterChain 都可以是唯一的,并且可以独立配置。实际上,如果应用程序希望 Spring Security 忽略某些请求,SecurityFilterChain 可能包含零个安全 Filter 实例。
安全过滤器
安全过滤器通过 SecurityFilterChain API 插入到 FilterChainProxy 中。这些过滤器可用于多种不同的目的,例如 漏洞防护、身份验证、授权 等。过滤器以特定顺序执行,以确保它们在正确的时间被调用,例如,执行身份验证的 Filter 应在执行授权的 Filter 之前被调用。通常不需要知道 Spring Security Filter 的顺序。但是,有时了解顺序会很有益,如果您想了解它们,可以查看 FilterOrderRegistration 代码。
这些安全过滤器最常使用 HttpSecurity 实例声明。为了说明上一段,我们考虑以下安全配置
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.csrf(Customizer.withDefaults())
.httpBasic(Customizer.withDefaults())
.formLogin(Customizer.withDefaults())
.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize
.anyRequest().authenticated()
);
return http.build();
}
}import org.springframework.security.config.web.servlet.invoke
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
fun filterChain(http: HttpSecurity): SecurityFilterChain {
http {
csrf { }
httpBasic { }
formLogin { }
authorizeHttpRequests {
authorize(anyRequest, authenticated)
}
}
return http.build()
}
}上述配置将导致以下 Filter 排序
| 过滤器 | 添加者 |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
首先,调用
CsrfFilter以防范 CSRF 攻击。 -
其次,调用认证过滤器以认证请求。
-
第三,调用
AuthorizationFilter以授权请求。
|
可能还有其他未列出的 |
打印安全过滤器
通常,查看特定请求调用的安全 Filter 列表很有用。例如,您希望确保您添加的过滤器在安全过滤器列表中。
过滤器列表在应用程序启动时以 DEBUG 级别打印,因此您可以在控制台输出上看到类似以下内容,例如
2023-06-14T08:55:22.321-03:00 DEBUG 76975 --- [ main] o.s.s.web.DefaultSecurityFilterChain : Will secure any request with [ DisableEncodeUrlFilter, WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter, SecurityContextHolderFilter, HeaderWriterFilter, CsrfFilter, LogoutFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter, DefaultLoginPageGeneratingFilter, DefaultLogoutPageGeneratingFilter, BasicAuthenticationFilter, RequestCacheAwareFilter, SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestFilter, AnonymousAuthenticationFilter, ExceptionTranslationFilter, AuthorizationFilter]这将很好地说明为每个过滤器链配置的安全过滤器。
但这并非全部,您还可以配置应用程序,使其为每个请求打印每个独立过滤器的调用。这有助于查看您添加的过滤器是否为特定请求调用,或检查异常的来源。为此,您可以配置应用程序以记录安全事件。
将过滤器添加到过滤器链
大多数情况下,默认的安全过滤器足以为您的应用程序提供安全保障。但是,有时您可能希望向SecurityFilterChain添加自定义 Filter。
HttpSecurity 带有三个添加过滤器的方法
-
#addFilterBefore(Filter, Class<?>)在另一个过滤器之前添加您的过滤器 -
#addFilterAfter(Filter, Class<?>)在另一个过滤器之后添加您的过滤器 -
#addFilterAt(Filter, Class<?>)用您的过滤器替换另一个过滤器
添加自定义过滤器
如果您正在创建自己的过滤器,您将需要确定它在过滤器链中的位置。请查看过滤器链中发生的以下关键事件
考虑您需要发生哪些事件才能找到您的过滤器。以下是一个经验法则
| 如果您的过滤器是 | 然后将其放置在 | 因为这些事件已经发生 |
|---|---|---|
漏洞防护过滤器 |
SecurityContextHolderFilter |
1 |
身份验证过滤器 |
LogoutFilter |
1, 2 |
授权过滤器 |
AnonymousAuthenticationFilter |
1, 2, 3 |
最常见的情况是,应用程序添加自定义身份验证。这意味着它们应该放置在 LogoutFilter 之后。 |
例如,假设您想要添加一个 Filter,它获取租户 ID 标头并检查当前用户是否具有访问该租户的权限。
首先,我们创建 Filter
import java.io.IOException;
import jakarta.servlet.Filter;
import jakarta.servlet.FilterChain;
import jakarta.servlet.ServletException;
import jakarta.servlet.ServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.ServletResponse;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.security.access.AccessDeniedException;
public class TenantFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) servletResponse;
String tenantId = request.getHeader("X-Tenant-Id"); (1)
boolean hasAccess = isUserAllowed(tenantId); (2)
if (hasAccess) {
filterChain.doFilter(request, response); (3)
return;
}
throw new AccessDeniedException("Access denied"); (4)
}
}上面的示例代码执行以下操作
| 1 | 从请求头中获取租户 ID。 |
| 2 | 检查当前用户是否具有访问租户 ID 的权限。 |
| 3 | 如果用户有权访问,则调用链中的其余过滤器。 |
| 4 | 如果用户无权访问,则抛出 AccessDeniedException。 |
|
您可以通过扩展 OncePerRequestFilter 来代替实现 |
现在,您需要将过滤器添加到 SecurityFilterChain。前面的描述已经给我们一个关于在哪里添加过滤器的线索,因为我们需要知道当前用户,所以我们需要在认证过滤器之后添加它。
根据经验法则,将其添加到链中最后一个认证过滤器 AnonymousAuthenticationFilter 之后,如下所示
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
// ...
.addFilterAfter(new TenantFilter(), AnonymousAuthenticationFilter.class); (1)
return http.build();
}@Bean
fun filterChain(http: HttpSecurity): SecurityFilterChain {
http
// ...
.addFilterAfter(TenantFilter(), AnonymousAuthenticationFilter::class.java) (1)
return http.build()
}| 1 | 使用 HttpSecurity#addFilterAfter 在 AnonymousAuthenticationFilter 之后添加 TenantFilter。 |
通过在 AnonymousAuthenticationFilter 之后添加过滤器,我们确保 TenantFilter 在认证过滤器之后被调用。
就这样,现在 TenantFilter 将在过滤器链中被调用,并将检查当前用户是否具有访问租户 ID 的权限。
将您的过滤器声明为 Bean
当您将 Filter 声明为 Spring bean 时,无论是通过使用 @Component 注解还是在您的配置中将其声明为 bean,Spring Boot 都会自动将其注册到嵌入式容器。这可能导致过滤器被调用两次,一次由容器调用,一次由 Spring Security 调用,并且顺序不同。
因此,过滤器通常不是 Spring bean。
但是,如果您的过滤器需要成为一个 Spring Bean(例如,为了利用依赖注入),您可以告诉 Spring Boot 不要将其注册到容器中,方法是声明一个 FilterRegistrationBean Bean 并将其 enabled 属性设置为 false
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean<TenantFilter> tenantFilterRegistration(TenantFilter filter) {
FilterRegistrationBean<TenantFilter> registration = new FilterRegistrationBean<>(filter);
registration.setEnabled(false);
return registration;
}这样就只有 HttpSecurity 添加它了。
自定义 Spring Security 过滤器
通常,您可以使用过滤器的 DSL 方法来配置 Spring Security 的过滤器。例如,添加 BasicAuthenticationFilter 的最简单方法是让 DSL 完成它
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.httpBasic(Customizer.withDefaults())
// ...
return http.build();
}@Bean
fun filterChain(http: HttpSecurity): SecurityFilterChain {
http {
httpBasic { }
// ...
}
return http.build()
}但是,如果您想自己构建 Spring Security 过滤器,您可以使用 addFilterAt 在 DSL 中指定它,如下所示
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
BasicAuthenticationFilter basic = new BasicAuthenticationFilter();
// ... configure
http
// ...
.addFilterAt(basic, BasicAuthenticationFilter.class);
return http.build();
}@Bean
fun filterChain(http: HttpSecurity): SecurityFilterChain {
val basic = BasicAuthenticationFilter()
// ... configure
http
// ...
.addFilterAt(basic, BasicAuthenticationFilter::class.java)
return http.build()
}请注意,如果该过滤器已被添加,Spring Security 将抛出异常。例如,调用 HttpSecurity#httpBasic 会为您添加一个 BasicAuthenticationFilter。因此,以下安排将失败,因为有两个调用都试图添加 BasicAuthenticationFilter
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
BasicAuthenticationFilter basic = new BasicAuthenticationFilter();
// ... configure
http
.httpBasic(Customizer.withDefaults())
// ... on no! BasicAuthenticationFilter is added twice!
.addFilterAt(basic, BasicAuthenticationFilter.class);
return http.build();
}@Bean
fun filterChain(http: HttpSecurity): SecurityFilterChain {
val basic = BasicAuthenticationFilter()
// ... configure
http {
httpBasic { }
}
// ... on no! BasicAuthenticationFilter is added twice!
http.addFilterAt(basic, BasicAuthenticationFilter::class.java)
return http.build()
}在这种情况下,由于您是自己构建 BasicAuthenticationFilter,因此请删除对 httpBasic 的调用。
|
如果您无法重新配置 |
处理安全异常
ExceptionTranslationFilter 允许将 AccessDeniedException 和 AuthenticationException 转换为 HTTP 响应。
ExceptionTranslationFilter 作为安全过滤器之一插入到FilterChainProxy中。
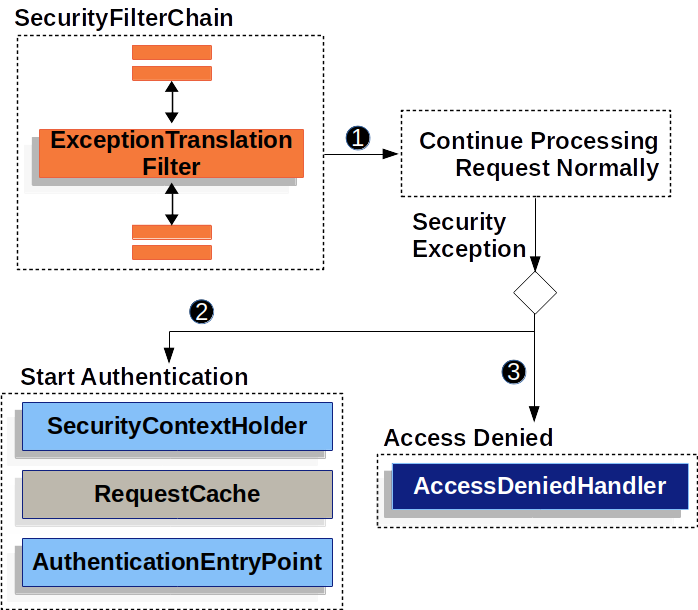
下图显示了 ExceptionTranslationFilter 与其他组件的关系
-
 首先,
首先,ExceptionTranslationFilter调用FilterChain.doFilter(request, response)来调用应用程序的其余部分。 -
 如果用户未认证或发生
如果用户未认证或发生 AuthenticationException,则开始认证。-
HttpServletRequest被保存,以便在认证成功后可以重放原始请求。 -
AuthenticationEntryPoint用于从客户端请求凭据。例如,它可能重定向到登录页面或发送WWW-Authenticate头。
-
 否则,如果发生
否则,如果发生 AccessDeniedException,则访问被拒绝。调用AccessDeniedHandler处理访问被拒绝。
|
如果应用程序没有抛出 |
ExceptionTranslationFilter 的伪代码看起来像这样
try {
filterChain.doFilter(request, response); (1)
} catch (AccessDeniedException | AuthenticationException ex) {
if (!authenticated || ex instanceof AuthenticationException) {
startAuthentication(); (2)
} else {
accessDenied(); (3)
}
}| 1 | 如 过滤器回顾 中所述,调用 FilterChain.doFilter(request, response) 等同于调用应用程序的其余部分。这意味着如果应用程序的其他部分(AuthorizationFilter 或方法安全性)抛出 AuthenticationException 或 AccessDeniedException,它将在此处被捕获和处理。 |
| 2 | 如果用户未认证或发生 AuthenticationException,则开始认证。 |
| 3 | 否则,访问被拒绝 |
认证之间保存请求
正如 处理安全异常 中所述,当请求没有认证并且请求的资源需要认证时,需要保存认证资源请求,以便在认证成功后重新请求。在 Spring Security 中,这是通过使用 RequestCache 实现保存 HttpServletRequest 来完成的。
RequestCache
HttpServletRequest 保存在 RequestCache 中。当用户成功认证后,RequestCache 用于重放原始请求。RequestCacheAwareFilter 在用户认证后使用 RequestCache 获取保存的 HttpServletRequest,而 ExceptionTranslationFilter 在检测到 AuthenticationException 后,将用户重定向到登录端点之前,使用 RequestCache 保存 HttpServletRequest。
默认情况下,使用 HttpSessionRequestCache。以下代码演示了如何自定义 RequestCache 实现,该实现检查 HttpSession 中是否存在保存的请求(如果存在名为 continue 的参数)。
continue 参数存在时 RequestCache 才检查保存的请求-
Java
-
Kotlin
-
XML
@Bean
DefaultSecurityFilterChain springSecurity(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
HttpSessionRequestCache requestCache = new HttpSessionRequestCache();
requestCache.setMatchingRequestParameterName("continue");
http
// ...
.requestCache((cache) -> cache
.requestCache(requestCache)
);
return http.build();
}@Bean
open fun springSecurity(http: HttpSecurity): SecurityFilterChain {
val httpRequestCache = HttpSessionRequestCache()
httpRequestCache.setMatchingRequestParameterName("continue")
http {
requestCache {
requestCache = httpRequestCache
}
}
return http.build()
}<http auto-config="true">
<!-- ... -->
<request-cache ref="requestCache"/>
</http>
<b:bean id="requestCache" class="org.springframework.security.web.savedrequest.HttpSessionRequestCache"
p:matchingRequestParameterName="continue"/>阻止请求被保存
您可能希望不将用户的未认证请求存储在会话中有多种原因。您可能希望将存储卸载到用户的浏览器中,或者将其存储在数据库中。或者您可能希望关闭此功能,因为您总是希望将用户重定向到主页,而不是他们在登录之前尝试访问的页面。
为此,您可以使用 NullRequestCache 实现。
-
Java
-
Kotlin
-
XML
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain springSecurity(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
RequestCache nullRequestCache = new NullRequestCache();
http
// ...
.requestCache((cache) -> cache
.requestCache(nullRequestCache)
);
return http.build();
}@Bean
open fun springSecurity(http: HttpSecurity): SecurityFilterChain {
val nullRequestCache = NullRequestCache()
http {
requestCache {
requestCache = nullRequestCache
}
}
return http.build()
}<http auto-config="true">
<!-- ... -->
<request-cache ref="nullRequestCache"/>
</http>
<b:bean id="nullRequestCache" class="org.springframework.security.web.savedrequest.NullRequestCache"/>RequestCacheAwareFilter
RequestCacheAwareFilter 使用 RequestCache 重放原始请求。
日志
Spring Security 提供所有安全相关事件的全面日志记录,级别为 DEBUG 和 TRACE。这在调试应用程序时非常有用,因为出于安全考虑,Spring Security 不会在响应正文中添加任何关于请求被拒绝的详细信息。如果您遇到 401 或 403 错误,您很可能会找到一条日志消息,帮助您了解发生了什么。
我们考虑一个示例,其中用户尝试向启用了 CSRF 保护 的资源发出 POST 请求,但没有 CSRF 令牌。在没有日志的情况下,用户将看到 403 错误,但没有解释请求被拒绝的原因。但是,如果您为 Spring Security 启用日志记录,您将看到类似以下的日志消息
2023-06-14T09:44:25.797-03:00 DEBUG 76975 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.s.security.web.FilterChainProxy : Securing POST /hello
2023-06-14T09:44:25.797-03:00 TRACE 76975 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.s.security.web.FilterChainProxy : Invoking DisableEncodeUrlFilter (1/15)
2023-06-14T09:44:25.798-03:00 TRACE 76975 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.s.security.web.FilterChainProxy : Invoking WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter (2/15)
2023-06-14T09:44:25.800-03:00 TRACE 76975 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.s.security.web.FilterChainProxy : Invoking SecurityContextHolderFilter (3/15)
2023-06-14T09:44:25.801-03:00 TRACE 76975 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.s.security.web.FilterChainProxy : Invoking HeaderWriterFilter (4/15)
2023-06-14T09:44:25.802-03:00 TRACE 76975 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.s.security.web.FilterChainProxy : Invoking CsrfFilter (5/15)
2023-06-14T09:44:25.814-03:00 DEBUG 76975 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.s.security.web.csrf.CsrfFilter : Invalid CSRF token found for https://:8080/hello
2023-06-14T09:44:25.814-03:00 DEBUG 76975 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.s.s.w.access.AccessDeniedHandlerImpl : Responding with 403 status code
2023-06-14T09:44:25.814-03:00 TRACE 76975 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.s.s.w.header.writers.HstsHeaderWriter : Not injecting HSTS header since it did not match request to [Is Secure]很明显,CSRF 令牌缺失,这就是请求被拒绝的原因。
要配置您的应用程序以记录所有安全事件,您可以将以下内容添加到您的应用程序中
logging.level.org.springframework.security=TRACE<configuration>
<appender name="STDOUT" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<!-- ... -->
</appender>
<!-- ... -->
<logger name="org.springframework.security" level="trace" additivity="false">
<appender-ref ref="Console" />
</logger>
</configuration>
