函数调用 API
在 AI 模型中集成函数支持,允许模型请求执行客户端函数,从而根据需要动态访问必要的信息或执行任务。
Spring AI 目前支持以下 AI 模型的函数调用
-
Anthropic Claude:请参阅Anthropic Claude 函数调用文档。
-
Azure OpenAI:请参阅Azure OpenAI 函数调用文档。
-
Google VertexAI Gemini:请参阅Vertex AI Gemini 函数调用文档。
-
Groq:请参阅Groq 函数调用文档。
-
Mistral AI:请参阅Mistral AI 函数调用文档。
-
Ollama:请参阅Ollama 函数调用文档(尚不支持流式传输)。
-
OpenAI:请参阅OpenAI 函数调用文档。
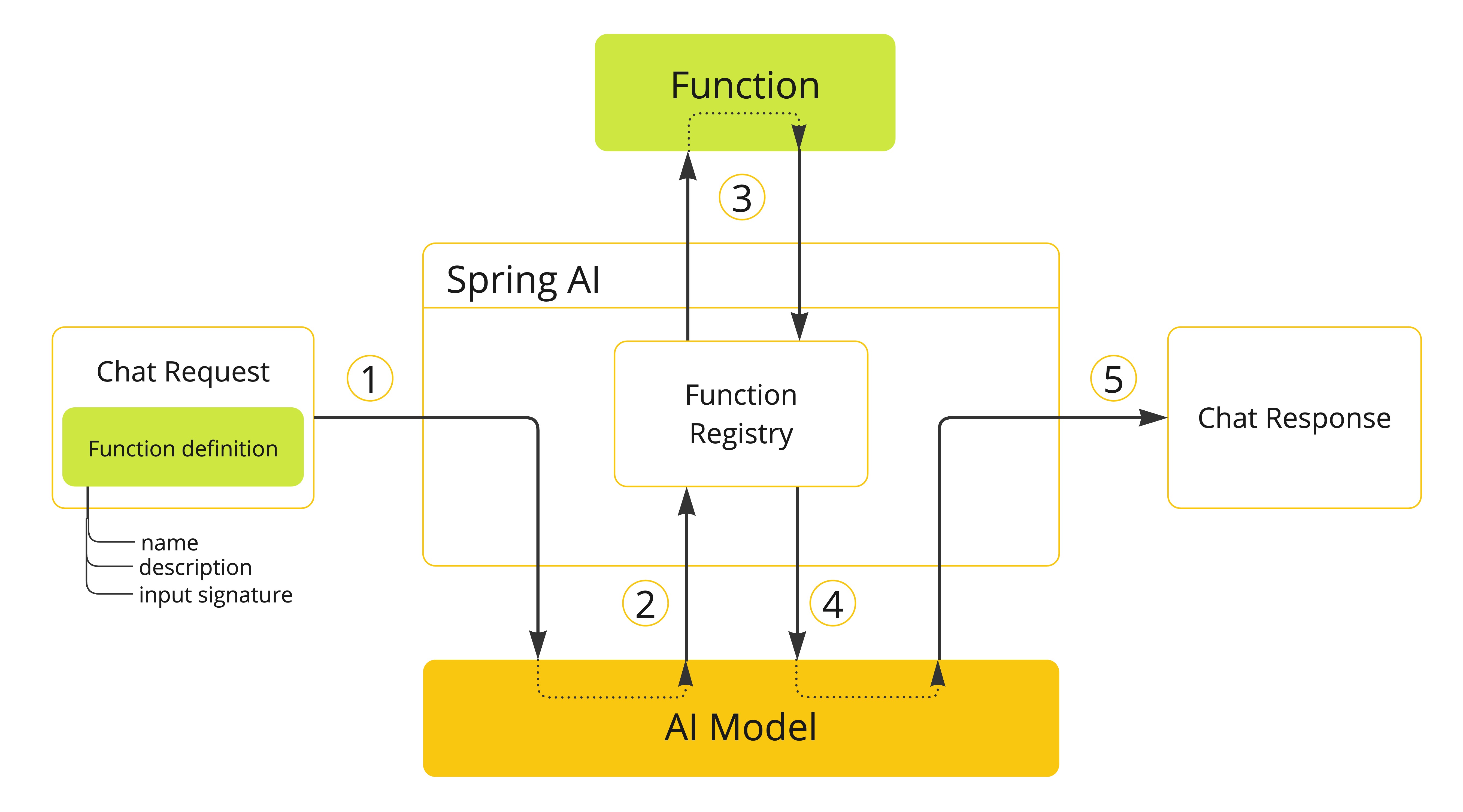
您可以使用 ChatClient 注册自定义 Java 函数,并让 AI 模型智能地选择输出包含要调用一个或多个已注册函数的参数的 JSON 对象。这允许您将 LLM 功能与外部工具和 API 连接起来。AI 模型经过训练可以检测何时应调用函数,并以符合函数签名的 JSON 响应。
API 不会直接调用函数;相反,模型会生成 JSON,您可以使用它在代码中调用函数并将结果返回给模型以完成对话。
Spring AI 提供了灵活且用户友好的方法来注册和调用自定义函数。通常,自定义函数需要提供函数 名称、描述和函数调用 签名(作为 JSON 模式),以让模型知道函数期望的参数。描述有助于模型理解何时调用函数。
作为开发人员,您需要实现一个函数,该函数接收来自 AI 模型的函数调用参数,并向模型返回结果。您的函数可以依次调用其他第三方服务来提供结果。
Spring AI 使此操作变得非常简单,只需定义一个返回 java.util.Function 的 @Bean 定义,并在调用 ChatClient 或在提示请求中动态注册函数时提供 bean 名称作为选项即可。
在底层,Spring 将您的 POJO(函数)与适当的适配器代码包装起来,从而能够与 AI 模型交互,从而节省了您编写冗长的样板代码的工作。底层基础设施的基础是FunctionCallback.java 接口以及配套的 Builder 实用程序类,用于简化 Java 回调函数的实现和注册。
工作原理
假设我们希望 AI 模型以它没有的信息进行响应,例如,给定位置的当前温度。
我们可以为 AI 模型提供有关我们自己的函数的元数据,它可以在处理您的提示时使用这些元数据来检索该信息。
例如,如果在处理提示的过程中,AI 模型确定它需要有关给定位置温度的更多信息,它将启动服务器端生成的请求/响应交互。AI 模型不会返回最终的响应消息,而是返回特殊的工具调用请求,提供函数名称和参数(作为 JSON)。客户端有责任处理此消息并执行命名函数,并将响应作为工具响应消息返回到 AI 模型。
Spring AI 极大地简化了您需要编写的支持函数调用的代码。它为您代理函数调用对话。您只需将函数定义作为 @Bean 提供,然后在提示选项中提供函数的 bean 名称,或者在提示请求选项中将函数直接作为参数传递。
您还可以在提示中引用多个函数 bean 名称。
示例用例
让我们定义一个简单的用例,我们可以用它作为示例来解释函数调用是如何工作的。让我们创建一个聊天机器人,通过调用我们自己的函数来回答问题。为了支持聊天机器人的响应,我们将注册我们自己的函数,该函数接受一个位置并返回该位置的当前天气。
当模型需要回答诸如"What’s the weather like in Boston?"这样的问题时,AI 模型将调用客户端,并将位置值作为参数传递给函数。这种类似 RPC 的数据以 JSON 格式传递。
我们的函数调用一些基于 SaaS 的天气服务 API,并将天气响应返回给模型以完成对话。在这个示例中,我们将使用一个名为MockWeatherService的简单实现,它对各种位置的温度进行硬编码。
以下MockWeatherService类表示天气服务 API
-
Java
-
Kotlin
public class MockWeatherService implements Function<Request, Response> {
public enum Unit { C, F }
public record Request(String location, Unit unit) {}
public record Response(double temp, Unit unit) {}
public Response apply(Request request) {
return new Response(30.0, Unit.C);
}
}class MockWeatherService : Function1<Request, Response> {
override fun invoke(request: Request) = Response(30.0, Unit.C)
}
enum class Unit { C, F }
data class Request(val location: String, val unit: Unit) {}
data class Response(val temp: Double, val unit: Unit) {}服务器端注册
函数作为 Bean
Spring AI 提供多种方法将自定义函数注册为 Spring 上下文中的 Bean。
我们首先描述最友好的 POJO 选项。
普通函数
在这种方法中,您像定义任何其他 Spring 托管对象一样,在应用程序上下文中定义一个@Bean。
在内部,Spring AI ChatModel 将创建一个FunctionCallback的实例,该实例添加了通过 AI 模型调用它的逻辑。@Bean的名称用作函数名称。
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Configuration
static class Config {
@Bean
@Description("Get the weather in location") // function description
public Function<MockWeatherService.Request, MockWeatherService.Response> currentWeather() {
return new MockWeatherService();
}
}@Configuration
class Config {
@Bean
@Description("Get the weather in location") // function description
fun currentWeather(): (Request) -> Response = MockWeatherService()
}@Description注释是可选的,它提供了一个函数描述,帮助模型理解何时调用该函数。这是一个需要设置的重要属性,以帮助 AI 模型确定要调用哪个客户端函数。
提供函数描述的另一种方法是在MockWeatherService.Request上使用@JsonClassDescription注释。
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Configuration
static class Config {
@Bean
public Function<Request, Response> currentWeather() { // bean name as function name
return new MockWeatherService();
}
}
@JsonClassDescription("Get the weather in location") // function description
public record Request(String location, Unit unit) {}@Configuration
class Config {
@Bean
fun currentWeather(): (Request) -> Response { // bean name as function name
return MockWeatherService()
}
}
@JsonClassDescription("Get the weather in location") // function description
data class Request(val location: String, val unit: Unit)最佳实践是用信息来注释请求对象,以便该函数生成的 JSON 模式尽可能具有描述性,以帮助 AI 模型选择正确的函数来调用。
FunctionCallback
注册函数的另一种方法是创建一个FunctionCallback,如下所示
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Configuration
static class Config {
@Bean
public FunctionCallback weatherFunctionInfo() {
return FunctionCallback.builder()
.description("Get the weather in location") // (2) function description
.function("CurrentWeather", new MockWeatherService()) // (1) function name and instance
.inputType(MockWeatherService.Request.class) // (3) input type to build the JSON schema
.build();
}
}import org.springframework.ai.model.function.withInputType
@Configuration
class Config {
@Bean
fun weatherFunctionInfo(): FunctionCallback {
return FunctionCallback.builder()
.description("Get the weather in location") // (2) function description
.function("CurrentWeather", MockWeatherService()) // (1) function name and instance
// (3) Required due to Kotlin SAM conversion being an opaque lambda
.inputType<MockWeatherService.Request>()
.build();
}
}它封装了第三方MockWeatherService函数并将其注册为ChatClient的CurrentWeather函数。它还提供了一个描述(2)和一个可选的响应转换器,用于将响应转换为模型期望的文本。
| 默认情况下,响应转换器执行 Response 对象的 JSON 序列化。 |
FunctionCallback.Builder在内部根据MockWeatherService.Request类解析函数调用签名。 |
按 Bean 名称启用函数
要让模型知道并调用您的CurrentWeather函数,您需要在提示请求中启用它
ChatClient chatClient = ...
ChatResponse response = this.chatClient.prompt("What's the weather like in San Francisco, Tokyo, and Paris?")
.functions("CurrentWeather") // Enable the function
.call().
chatResponse();
logger.info("Response: {}", response);上述用户问题将触发对CurrentWeather函数的 3 次调用(每个城市一次),最终响应将类似于以下内容
Here is the current weather for the requested cities: - San Francisco, CA: 30.0°C - Tokyo, Japan: 10.0°C - Paris, France: 15.0°C
该FunctionCallbackWithPlainFunctionBeanIT.java测试演示了这种方法。
客户端注册
除了自动配置之外,您还可以动态注册回调函数。您可以使用函数调用或方法调用方法将函数注册到您的ChatClient或ChatModel请求中。
客户端注册允许您默认注册函数。
函数调用
ChatClient chatClient = ...
ChatResponse response = this.chatClient.prompt("What's the weather like in San Francisco, Tokyo, and Paris?")
.functions(FunctionCallback.builder()
.description("Get the weather in location") // (2) function description
.function("currentWeather", (Request request) -> new Response(30.0, Unit.C)) // (1) function name and instance
.inputType(MockWeatherService.Request.class) // (3) input type to build the JSON schema
.build())
.call()
.chatResponse();| 此请求期间默认启用动态函数。 |
这种方法允许根据用户输入动态选择要调用的不同函数。
该FunctionCallbackInPromptIT.java集成测试提供了一个完整的示例,说明如何使用ChatClient注册函数并在提示请求中使用它。
方法调用
MethodInvokingFunctionCallback允许通过反射进行方法调用,同时自动处理 JSON 模式生成和参数转换。它对于将 Java 方法作为可调用函数集成到 AI 模型交互中特别有用。
MethodInvokingFunctionCallback实现了FunctionCallback接口并提供
-
方法参数的自动 JSON 模式生成
-
支持静态方法和实例方法
-
任意数量的参数(包括无)和返回值(包括 void)
-
任何参数/返回类型(基本类型、对象、集合)
-
对
ToolContext参数的特殊处理
您需要FunctionCallback.Builder来创建MethodInvokingFunctionCallback,如下所示
// Create using builder pattern
FunctionCallback methodInvokingCallback = FunctionCallback.builder()
.description("Function calling description") // Hints the AI to know when to call this method
.method("MethodName", Class<?>...argumentTypes) // The method to invoke and its argument types
.targetObject(targetObject) // Required instance methods for static methods use targetClass
.build();以下是一些使用示例
-
静态方法调用
-
带 ToolContext 的实例方法
public class WeatherService {
public static String getWeather(String city, TemperatureUnit unit) {
return "Temperature in " + city + ": 20" + unit;
}
}
// Usage
FunctionCallback callback = FunctionCallback.builder()
.description("Get weather information for a city")
.method("getWeather", String.class, TemperatureUnit.class)
.targetClass(WeatherService.class)
.build();public class DeviceController {
public void setDeviceState(String deviceId, boolean state, ToolContext context) {
Map<String, Object> contextData = context.getContext();
// Implementation using context data
}
}
// Usage
DeviceController controller = new DeviceController();
String response = ChatClient.create(chatModel).prompt()
.user("Turn on the living room lights")
.functions(FunctionCallback.builder()
.description("Control device state")
.method("setDeviceState", String.class,boolean.class,ToolContext.class)
.targetObject(controller)
.build())
.toolContext(Map.of("location", "home"))
.call()
.content();该OpenAiChatClientMethodInvokingFunctionCallbackIT集成测试提供了如何使用 FunctionCallback.Builder 创建方法调用 FunctionCallback 的其他示例。
工具上下文
Spring AI 现在支持通过工具上下文将其他上下文信息传递给函数回调。此功能允许您提供额外的用户提供的数据,这些数据可以在函数执行过程中与 AI 模型传递的函数参数一起使用。
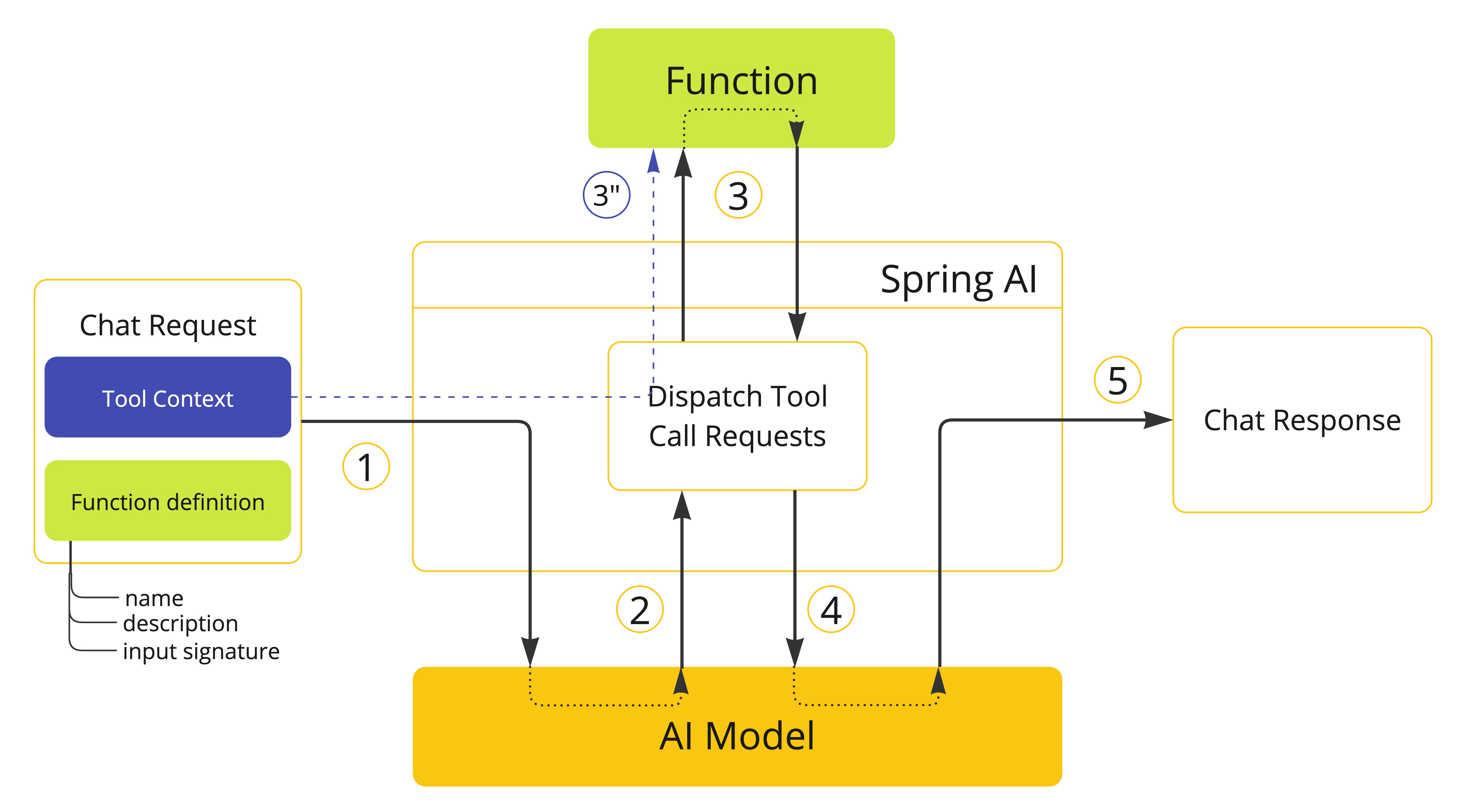
该ToolContext类提供了一种传递其他上下文信息的方法。
使用工具上下文
在函数调用情况下,作为java.util.BiFunction的第二个参数传递的上下文信息。
对于方法调用,上下文信息作为类型为ToolContext的方法参数传递。
函数调用
您可以在构建聊天选项时设置工具上下文,并为回调使用 BiFunction
BiFunction<MockWeatherService.Request, ToolContext, MockWeatherService.Response> weatherFunction =
(request, toolContext) -> {
String sessionId = (String) toolContext.getContext().get("sessionId");
String userId = (String) toolContext.getContext().get("userId");
// Use sessionId and userId in your function logic
double temperature = 0;
if (request.location().contains("Paris")) {
temperature = 15;
}
else if (request.location().contains("Tokyo")) {
temperature = 10;
}
else if (request.location().contains("San Francisco")) {
temperature = 30;
}
return new MockWeatherService.Response(temperature, 15, 20, 2, 53, 45, MockWeatherService.Unit.C);
};
ChatResponse response = chatClient.prompt("What's the weather like in San Francisco, Tokyo, and Paris?")
.functions(FunctionCallback.builder()
.description("Get the weather in location")
.function("getCurrentWeather", this.weatherFunction)
.inputType(MockWeatherService.Request.class)
.build())
.toolContext(Map.of("sessionId", "1234", "userId", "5678"))
.call()
.chatResponse();在此示例中,weatherFunction被定义为一个 BiFunction,它将请求和工具上下文作为参数。这允许您直接在函数逻辑中访问上下文。
这种方法允许您将特定于会话或特定于用户的信息传递给您的函数,从而实现更具上下文和个性化的响应。
方法调用
public class DeviceController {
public void setDeviceState(String deviceId, boolean state, ToolContext context) {
Map<String, Object> contextData = context.getContext();
// Implementation using context data
}
}
// Usage
DeviceController controller = new DeviceController();
String response = ChatClient.create(chatModel).prompt()
.user("Turn on the living room lights")
.functions(FunctionCallback.builder()
.description("Control device state")
.method("setDeviceState", String.class,boolean.class,ToolContext.class)
.targetObject(controller)
.build())
.toolContext(Map.of("location", "home"))
.call()
.content();
